C语言栈和队列如何实现
这篇文章主要讲解了“C语言栈和队列如何实现”,文中的讲解内容简单清晰,易于学习与理解,下面请大家跟着小编的思路慢慢深入,一起来研究和学习“C语言栈和队列如何实现”吧!
一、栈与队列以及双端队列的概念
1.1 栈的概念及结构
栈:一种特殊的线性表,其只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素操作。进行数据插入和删除操作的一端 称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。栈中的数据元素遵守后进先出LIFO(Last In First Out)的原则。
压栈:栈的插入操作叫做进栈/压栈/入栈,入数据在栈顶。
出栈:栈的删除操作叫做出栈。出数据也在栈顶
1.2 队列的概念及结构
队列:只允许在一端进行插入数据操作,在另一端进行删除数据操作的特殊线性表,队列具有先进先出 FIFO(First In First Out)
入队列:进行插入操作的一端称为队尾
出队列:进行删除操作的一端称为队头
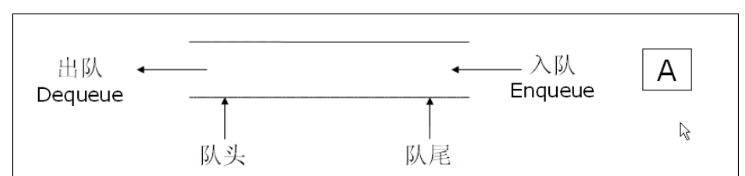
1.3 双端队列的概念及结构
双端队列:是一种线性表,又称为双向队列,所有的插入和删除(通常还有所有的访问)都在表的两端进行。
二、栈的实现和模拟栈
栈的实现一般可以使用数组或者链表实现,相对而言数组的结构实现更优一些。因为数组在尾上插入数据的 代价比较小。、
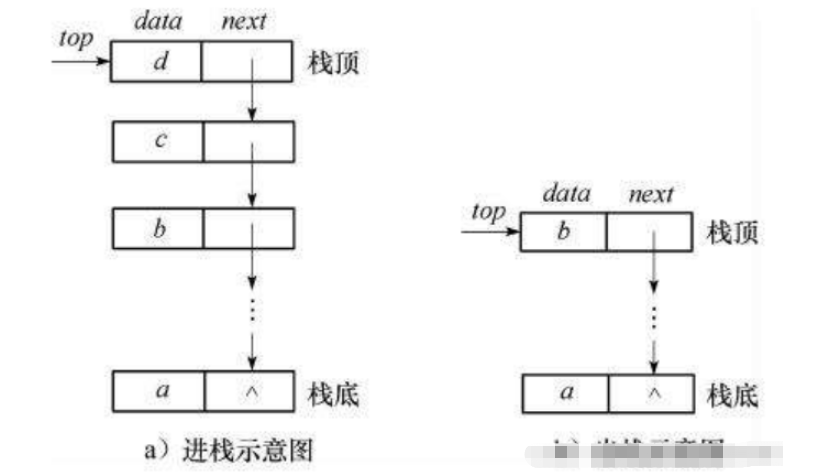
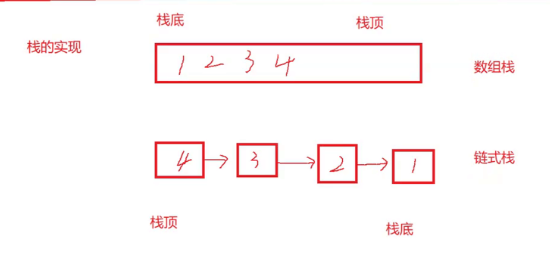
2.1 实现一个支持动态增长的栈
头文件:
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include<assert.h>
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack//动态栈
{
int *a;
int top;//栈顶的位置
int capacity;//容量
}ST;
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps);//返回栈顶的值
void StackInit(ST* ps);//初始化栈
void StackDestory(ST* ps);//销毁栈
void StackPop(ST* ps);//弹出
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x);//插入
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps);//判断栈是否为空。
源文件:
#include"Stack.h"
void StackInit(ST* ps)//栈的初始化
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = NULL;//a点的值指向空
ps->top = 0;//栈底为0
ps->capacity = 0;//空间为0
}
void StackDestory(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);//把a释放掉
ps->a = NULL;
ps->capacity = ps->top = 0;
}
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)//入数据
{
assert(ps);
//满了就扩容
if (ps->top == ps->capacity)//如果栈的栈顶恰好和容量相等就扩容
{
int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
ps->a = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a, newCapacity * sizeof(STDataType));
if (ps->a == NULL)
{
printf("realloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
ps->capacity = newCapacity;//新的空间赋给旧的
}
ps->a[ps->top] = x;//栈顶插入x;
ps->top++;//top++
}
void StackPop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0);
--ps->top;//top--就相当于删除操作
}
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
//两种写法
//if (ps->top > 0)
//{
// return false;
//}
//else
//{
// return true;
//}
return ps->top == 0;
}
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0);
return ps->a[ps->top - 1];//访问栈顶元素(这里因为top我们设为0,所以访问栈顶元素相当于top-1
}
int StackSize(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}
2.2 数组模拟静态栈

#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e6 + 10;
int n;
int stk[N];
int top = - 1;
int main ()
{
cin >> n;
while(n --)
{
string s;
cin >> s;
if(s == "push")
{
int a;
cin >> a;
stk[++top] = a;
}
if(s == "pop")
{
top--;
}
if(s == "empty")
{
if(top >= 0) printf("NO\n");
else printf("YES\n");
}
if(s == "query")
{
printf("%d\n", stk[top]);
}
}
return 0;
}
三、 队列的实现(动态)和模拟静态队列
队列也可以数组和链表的结构实现,使用链表的结构实现更优一些,因为如果使用数组的结构,出队列在数 组头上出数据,效率会比较低。
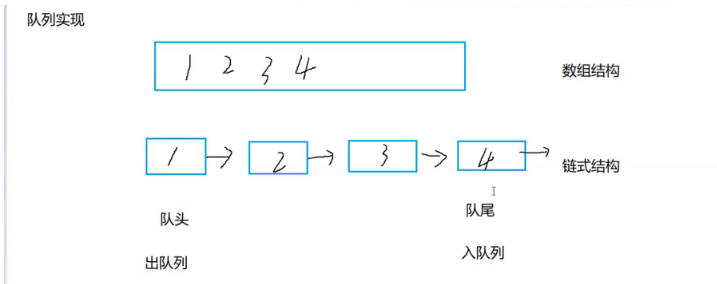
3.1 实现一个支持动态增长的栈
头文件:
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include<assert.h>
typedef int QDataType;//方便改类型
typedef struct QueueNode//保存每个节点的数据
{
QDataType data;
struct QueueNode* next;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* head;
QNode* tail;
}Queue;
//上面的写法等价于:
//typedef struct Queue
//{
// QNode* head;
// QNode* tail;
//};
//
//typedef struct Queue Queue;//
//一般实际情况哨兵位的头节点不存储值,不放数据
void QueueInit(Queue* pq);//队列初始化
void QueueDestory(Queue* pq);//队列销毁
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x);//队尾插入
void QueuePop(Queue* pq);//弹出队头
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);//判断是否为空
size_t QueueSize(Queue* pq);//size_t相当于Unsinged int
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq);
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq);
源文件:
#include"Queue.h"
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
void QueueDestory(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;//先记录下一个位置
free(cur);//free掉cur指针
cur = next;//cur赋值到下一个位置
}
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;//置空
}
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)//队尾插入//插入int类型的参数
{
assert(pq);
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
assert(newnode);
newnode->data = x;//新的节点的值被赋与x
newnode->next = NULL;//新的节点是在队尾,所以指向的下一个位置是空
if (pq->tail == NULL)//如果链表的第一个值为空,则head = tail = NULL
{
assert(pq->head == NULL);
pq->head = pq->tail = newnode;
}
else//尾插
{
pq->tail->next = newnode;//先改指向
pq->tail = newnode;//再改地址
}
}
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)//弹出队首
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->head && pq->tail);
if (pq->head->next == NULL)//只有一个节点
{
free(pq->head);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
else
{
QNode* next = pq->head->next;//QNode* next相当于是QDataType的头指针的下一个位置
free(pq->head);
pq->head = next;//头往后走
}
}
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
//return pq->head == NULL && pq->tail == NULL;
return pq->head == NULL;//程序调试了快一个小时就是因为pq->head没加后面的== NULL
}
size_t QueueSize(Queue* pq)//size_t相当于Unsinged int
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->head;
size_t size = 0;
while (cur)
{
size++;
cur = cur->next;
}
return size;
}
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)//返回队头第一个位的值
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->head);
return pq->head->data;
}
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)//返回队尾的值
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->tail);
return pq->tail->data;
}
3.2 数组模拟静态队列

#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e5 + 10;
int q[N];
int n;
int hh ,tt = -1;//hh表示头,tt表示尾
int main ()
{
cin >> n;
while(n --)
{
string s;
cin >> s;
if(s == "push")
{
int x;
cin >> x;
q[++tt] = x;
}
else if(s == "pop")
{
hh ++;
}
else if(s == "empty")
{
if(hh <= tt) printf("NO\n");//尾在逻辑上要比头更前面
else printf("YES\n");
}
else cout << q[hh] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
四、leetcode-栈实现队列和用队列实现栈
225. 用队列实现栈 - 力扣(LeetCode)

代码:
typedef int QDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode//保存每个节点的数据
{
QDataType data;
struct QueueNode* next;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* head;
QNode* tail;
}Queue;
void QueueInit(Queue* pq);
void QueueDestory(Queue* pq);
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x);//队尾插入
void QueuePop(Queue* pq);
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);
size_t QueueSize(Queue* pq);//size_t相当于Unsinged int
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq);
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq);
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
void QueueDestory(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;//先记录下一个位置
free(cur);//free掉cur指针
cur = next;//cur赋值到下一个位置
}
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;//置空
}
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)//队尾插入
{
assert(pq);
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
assert(newnode);
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
if (pq->tail == NULL)//如果链表的第一个值为空,则head = tail = NULL
{
assert(pq->head == NULL);
pq->head = pq->tail = newnode;
}
else//尾插
{
pq->tail->next = newnode;
pq->tail = newnode;
}
}
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)//弹出队首
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->head && pq->tail);
if (pq->head->next == NULL)//只有一个节点
{
free(pq->head);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
else
{
QNode* next = pq->head->next;//QNode* next相当于是QDataType的头指针的下一个位置
free(pq->head);
pq->head = next;//头往后走
}
}
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
//return pq->head == NULL && pq->tail == NULL;
return pq->head == NULL;//程序调试了快一个小时就是因为pq->head没加后面的== NULL
}
size_t QueueSize(Queue* pq)//size_t相当于Unsinged int
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->head;
size_t size = 0;
while (cur)
{
size++;
cur = cur->next;
}
return size;
}
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)//返回队头第一个位的值
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->head);
return pq->head->data;
}
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->tail);
return pq->tail->data;
}
typedef struct {
Queue q1;
Queue q2;
} MyStack;
MyStack* myStackCreate() {
MyStack* pst = (MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));
assert(pst);
QueueInit(&pst->q1);
QueueInit(&pst->q2);
return pst;
}
void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x) {
assert(obj);
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
QueuePush(&obj->q1, x);
}
else
{
QueuePush(&obj->q2, x);
}
}
int myStackPop(MyStack* obj) {
Queue* emptyQ = &obj->q1;//假设q1为空,q2不为空
Queue* nonEmptyQ = &obj->q2;
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))
{
emptyQ = &obj->q2;
nonEmptyQ = &obj->q1;
}
//把非空队列的前N个数据导入空队列,剩下一个删掉
//就实现了后进先出
while(QueueSize(nonEmptyQ) > 1)
{
QueuePush(emptyQ, QueueFront(nonEmptyQ));
QueuePop(nonEmptyQ);
}
int top = QueueFront(nonEmptyQ);//此时那个非空的队列只剩下一个数据
QueuePop(nonEmptyQ);
return top;
}
int myStackTop(MyStack* obj) {
assert(obj);
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->q1))//如果q1不为空
{
return QueueBack(&obj->q1);
}
else
{
return QueueBack(&obj->q2);
}
}
bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj) {
return QueueEmpty(&obj->q1) && QueueEmpty(&obj->q2);
}
void myStackFree(MyStack* obj) {
assert(obj);
QueueDestory(&obj->q1);
QueueDestory(&obj->q2);
free(obj);
}
232. 用栈实现队列 - 力扣(LeetCode)栈是后进先出
思路:设计两个栈,一个栈专门用来入数据,一个栈专门用来出数据。

typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack//动态链表
{
int *a;
int top;//栈顶的位置
int capacity;//容量
}ST;
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps);
void StackInit(ST* ps);//初始化栈
void StackDestory(ST* ps);
void StackPop(ST* ps);
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x);
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps);
void StackInit(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->top = 0;
ps->capacity = 0;
}
void StackDestory(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->capacity = ps->top = 0;
}
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)//入数据
{
assert(ps);
//满了就扩容
if (ps->top == ps->capacity)
{
int newCapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 2;
ps->a = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a, newCapacity * sizeof(STDataType));
if (ps->a == NULL)
{
printf("realloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
ps->capacity = newCapacity;
}
ps->a[ps->top] = x;
ps->top++;
}
void StackPop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0);
--ps->top;
}
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
//两种写法
//if (ps->top > 0)
//{
// return false;
//}
//else
//{
// return true;
//}
return ps->top == 0;
}
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0);
return ps->a[ps->top - 1];//访问栈顶元素
}
int StackSize(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}
typedef struct
{
ST pushST;
ST popST;
} MyQueue;
MyQueue* myQueueCreate() {
MyQueue* obj = (MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));
assert(obj);
StackInit(&obj->pushST);//&符要加,要改变结构体里面的内容
StackInit(&obj->popST);
return obj;
}
void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x) {
assert(obj);
StackPush(&obj->pushST, x);
}
int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj) {
assert(obj);
//如果popST为空, 把pushST的数据拿过来,就符合先进先出的顺序了
if(StackEmpty(&obj->popST))//如果ST Pop为空就执行
{
while(!StackEmpty(&obj->pushST))
{
StackPush(&obj->popST, StackTop(&obj->pushST));
StackPop(&obj->pushST);//把pushST里的数据删掉
}
}
int front = StackTop(&obj->popST);//记录栈顶的数据
StackPop(&obj->popST);
return front;
}
int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj) {
assert(obj);
//如果popST为空, 把pushST的数据拿过来,就符合先进先出的顺序了
if(StackEmpty(&obj->popST))//如果ST Pop为空就执行
{
while(!StackEmpty(&obj->pushST))
{
StackPush(&obj->popST, StackTop(&obj->pushST));
StackPop(&obj->pushST);//把pushST里的数据删掉
}
}
return StackTop(&obj->popST);
}
bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj) {
assert(obj);
return StackEmpty(&obj->pushST)&&StackEmpty(&obj->popST);
}
void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj) {
assert(obj);
StackDestory(&obj->pushST);
StackDestory(&obj->popST);
free(obj);
}
感谢各位的阅读,以上就是“C语言栈和队列如何实现”的内容了,经过本文的学习后,相信大家对C语言栈和队列如何实现这一问题有了更深刻的体会,具体使用情况还需要大家实践验证。这里是蜗牛博客,小编将为大家推送更多相关知识点的文章,欢迎关注!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:niceseo99@gmail.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。















评论