怎么用Python Pandas处理CSV文件
本篇内容主要讲解“怎么用Python Pandas处理CSV文件”,感兴趣的朋友不妨来看看。本文介绍的方法操作简单快捷,实用性强。下面就让小编来带大家学习“怎么用Python Pandas处理CSV文件”吧!
读取Pandas文件
df = pd.read_csv(file_path, encoding='GB2312') print(df.info())
注意:Pandas的读取格式默认是UTF-8,在中文CSV中会报错:
UnicodeDecodeError: 'utf-8' codec can't decode byte 0xd1 in position 2: invalid continuation byte
修改编码为 GB2312 ,即可,或者忽略encode转义错误,如下:
df = pd.read_csv(file_path, encoding='GB2312') df = pd.read_csv(file_path, encoding='unicode_escape')
df.info()显示df的基本信息,例如:
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
RangeIndex: 3840 entries, 0 to 3839
Data columns (total 16 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 实验时间批次 3840 non-null object
1 物镜倍数 3840 non-null object
2 板子编号 3840 non-null object
3 板子编号及物镜倍数 3840 non-null object
4 图名称 3840 non-null object
5 细胞类型 3840 non-null object
6 板子孔位置 3840 non-null object
7 孔拍摄位置 3840 non-null int64
8 细胞培养基 3840 non-null object
9 细胞培养时间(小时) 3840 non-null int64
10 扰动类别 3840 non-null object
11 扰动处理时间(小时) 3840 non-null int64
12 扰动处理浓度(ug/ml) 3840 non-null float64
13 标注激活(1/0) 3840 non-null int64
14 unique 3840 non-null object
15 tvt 3840 non-null int64
dtypes: float64(1), int64(5), object(10)
memory usage: 480.1+ KB
统计列值出现的次数
df[列名].value_counts(),如df["扰动类别"].value_counts():
df["扰动类别"].value_counts()
输出:
coated OKT3 720
OKT3 720
coated OKT3+anti-CD28 576
DMSO 336
anti-CD28 288
PBS 288
Nivo 288
Pemb 288
empty 192
coated OKT3 + anti-CD28 144
Name: 扰动类别, dtype: int64
直接绘制value_counts()的柱形图,参考Pandas - Chart Visualization:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline
plt.close("all")
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 8))
df["扰动类别"].value_counts().plot(kind="bar")
# plt.xticks(rotation='vertical', fontsize=10)
plt.show()
柱形图:
筛选特定列值
df.loc[筛选条件],筛选特定列值之后,重新赋值,只处理筛选值,也可以写入csv文件。
df_plate1 = df.loc[df["板子编号"] == "plate1"]
df_plate1.info()
# df.loc[df["板子编号"] == "plate1"].to_csv("batch4_IOStrain_klasses_utf8_plate1.csv") # 存储CSV文件
注意:筛选的内外两个df需要相同,否则报错
pandas loc IndexingError: Unalignable boolean Series provided as indexer (index of the boolean Series and of the indexed object do not match).
输出,数据量由3840下降为1280。
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'>
Int64Index: 1280 entries, 0 to 1279
Data columns (total 16 columns):
# Column Non-Null Count Dtype
--- ------ -------------- -----
0 实验时间批次 1280 non-null object
1 物镜倍数 1280 non-null object
2 板子编号 1280 non-null object
3 板子编号及物镜倍数 1280 non-null object
4 图名称 1280 non-null object
5 细胞类型 1280 non-null object
6 板子孔位置 1280 non-null object
7 孔拍摄位置 1280 non-null int64
8 细胞培养基 1280 non-null object
9 细胞培养时间(小时) 1280 non-null int64
10 扰动类别 1280 non-null object
11 扰动处理时间(小时) 1280 non-null int64
12 扰动处理浓度(ug/ml) 1280 non-null float64
13 标注激活(1/0) 1280 non-null int64
14 unique 1280 non-null object
15 tvt 1280 non-null int64
dtypes: float64(1), int64(5), object(10)
memory usage: 170.0+ KB
遍历数据行
for idx, row in df_plate1_lb0.iterrows():,通过row[“列名”],输出具体的值,如下:
for idx, row in df_plate1_lb0.iterrows():
img_name = row["图名称"]
img_ch_format = img_format.format(img_name, "{}")
for i in range(1, 7):
img_path = os.path.join(plate1_img_folder, img_ch_format.format(i))
img = cv2.imread(img_path)
print('[Info] img shape: {}'.format(img.shape))
break
输出:
[Info] img shape: (1080, 1080, 3)
[Info] img shape: (1080, 1080, 3)
[Info] img shape: (1080, 1080, 3)
[Info] img shape: (1080, 1080, 3)
[Info] img shape: (1080, 1080, 3)
[Info] img shape: (1080, 1080, 3)
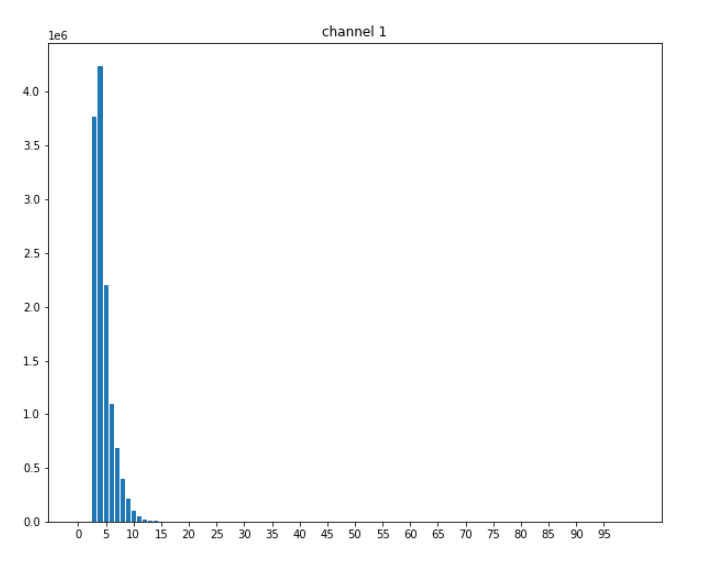
绘制直方图(柱状图)
统计去除背景颜色的灰度图字典
# 去除背景颜色 pix_bkg = np.argmax(np.bincount(img_gray.ravel())) img_gray = np.where(img_gray <= pix_bkg + 2, 0, img_gray) img_gray = img_gray.astype(np.uint8) # 生成数值数组 hist = cv2.calcHist([img_gray], [0], None, [256], [0, 256]) hist = hist.ravel() # 数值字典 hist_dict = collections.defaultdict(int) for i, v in enumerate(hist): hist_dict[i] += int(v) # 去除背景颜色,已经都统计到0,所以0值非常大,删除0值,观察分布 hist_dict[0] = 0
绘制柱状图:
plt.subplots:设置多个子图,figsize背景尺寸,facecolor背景颜色
ax.set_title:设置标题
ax.bar:x轴的值,y轴的值
ax.set_xticks:x轴的显示间隔
plt.savefig:存储图像
plt.show:展示
fig, ax = plt.subplots(1, 1, figsize=(10, 8), facecolor='white')
ax.set_title('channel {}'.format(ci))
n_bins = 100
ax.bar(range(n_bins+1), [hist_dict.get(xtick, 0) for xtick in range(n_bins+1)])
ax.set_xticks(range(0, n_bins, 5))
plt.savefig(res_path)
plt.show()
效果:
到此,相信大家对“怎么用Python Pandas处理CSV文件”有了更深的了解,不妨来实际操作一番吧!这里是蜗牛博客网站,更多相关内容可以进入相关频道进行查询,关注我们,继续学习!
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:niceseo99@gmail.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。














评论