Python first-order-model怎么实现让照片动起来
这篇文章主要介绍“Python first-order-model怎么实现让照片动起来”的相关知识,小编通过实际案例向大家展示操作过程,操作方法简单快捷,实用性强,希望这篇“Python first-order-model怎么实现让照片动起来”文章能帮助大家解决问题。
资源下载和安装
我们先看一下README关于项目的基本信息,可以看出除了表情驱动照片,还可以姿态迁移。
模型文件提供了线上的下载地址。
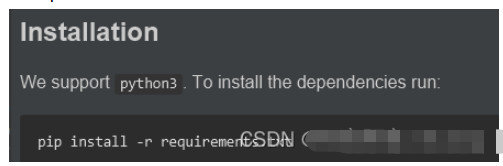
将requirements.txt中的依赖安装一下。
安装补充
在测试README中的命令的时候,如果出现一下报错。
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "demo.py", line 17, in <module>
from animate import normalize_kp
File "D:\spyder\first-order-model\animate.py", line 7, in <module>
from frames_dataset import PairedDataset
File "D:\spyder\first-order-model\frames_dataset.py", line 10, in <module>
from augmentation import AllAugmentationTransform
File "D:\spyder\first-order-model\augmentation.py", line 13, in <module>
import torchvision
File "C:\Users\huyi\.conda\envs\fom\lib\site-packages\torchvision\__init__.py", line 2, in <module>
from torchvision import datasets
File "C:\Users\huyi\.conda\envs\fom\lib\site-packages\torchvision\datasets\__init__.py", line 9, in <module>
from .fakedata import FakeData
File "C:\Users\huyi\.conda\envs\fom\lib\site-packages\torchvision\datasets\fakedata.py", line 3, in <module>
from .. import transforms
File "C:\Users\huyi\.conda\envs\fom\lib\site-packages\torchvision\transforms\__init__.py", line 1, in <module>
from .transforms import *
File "C:\Users\huyi\.conda\envs\fom\lib\site-packages\torchvision\transforms\transforms.py", line 16, in <module>
from . import functional as F
File "C:\Users\huyi\.conda\envs\fom\lib\site-packages\torchvision\transforms\functional.py", line 5, in <module>
from PIL import Image, ImageOps, ImageEnhance, PILLOW_VERSION
ImportError: cannot import name 'PILLOW_VERSION' from 'PIL' (C:\Users\huyi\.conda\envs\fom\lib\site-packages\PIL\__init__.py)
这个问题主要是我使用的pillow版本过高的原因,如果不想找对应的低版本,可以按照我的方式解决。
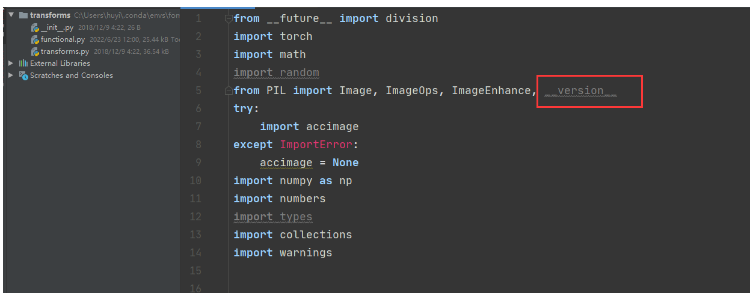
1、修改functional.py代码,将PILLOW_VERSION调整为__version__。
2、将imageio升级。
pip install --upgrade imageio -i https://pypi.douban.com/simple
3、安装imageio_ffmpeg模块。
pip install imageio-ffmpeg -i https://pypi.douban.com/simple
工具代码验证
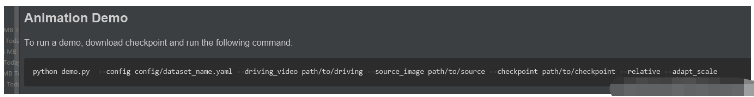
官方给出的使用方法我就不重复测试,大家可以按照下面的命令去测试一下。
这里我推荐一个可视化的库gradio,下面我将demo.py的代码改造了一下。
新的工具文件代码如下:
#!/user/bin/env python
# coding=utf-8
"""
@project : first-order-model
@author : 剑客阿良_ALiang
@file : hy_gradio.py
@ide : PyCharm
@time : 2022-06-23 14:35:28
"""
import uuid
from typing import Optional
import gradio as gr
import matplotlib
matplotlib.use('Agg')
import os, sys
import yaml
from argparse import ArgumentParser
from tqdm import tqdm
import imageio
import numpy as np
from skimage.transform import resize
from skimage import img_as_ubyte
import torch
from sync_batchnorm import DataParallelWithCallback
from modules.generator import OcclusionAwareGenerator
from modules.keypoint_detector import KPDetector
from animate import normalize_kp
from scipy.spatial import ConvexHull
if sys.version_info[0] < 3:
raise Exception("You must use Python 3 or higher. Recommended version is Python 3.7")
def load_checkpoints(config_path, checkpoint_path, cpu=False):
with open(config_path) as f:
config = yaml.load(f)
generator = OcclusionAwareGenerator(**config['model_params']['generator_params'],
**config['model_params']['common_params'])
if not cpu:
generator.cuda()
kp_detector = KPDetector(**config['model_params']['kp_detector_params'],
**config['model_params']['common_params'])
if not cpu:
kp_detector.cuda()
if cpu:
checkpoint = torch.load(checkpoint_path, map_location=torch.device('cpu'))
else:
checkpoint = torch.load(checkpoint_path)
generator.load_state_dict(checkpoint['generator'])
kp_detector.load_state_dict(checkpoint['kp_detector'])
if not cpu:
generator = DataParallelWithCallback(generator)
kp_detector = DataParallelWithCallback(kp_detector)
generator.eval()
kp_detector.eval()
return generator, kp_detector
def make_animation(source_image, driving_video, generator, kp_detector, relative=True, adapt_movement_scale=True,
cpu=False):
with torch.no_grad():
predictions = []
source = torch.tensor(source_image[np.newaxis].astype(np.float32)).permute(0, 3, 1, 2)
if not cpu:
source = source.cuda()
driving = torch.tensor(np.array(driving_video)[np.newaxis].astype(np.float32)).permute(0, 4, 1, 2, 3)
kp_source = kp_detector(source)
kp_driving_initial = kp_detector(driving[:, :, 0])
for frame_idx in tqdm(range(driving.shape[2])):
driving_frame = driving[:, :, frame_idx]
if not cpu:
driving_frame = driving_frame.cuda()
kp_driving = kp_detector(driving_frame)
kp_norm = normalize_kp(kp_source=kp_source, kp_driving=kp_driving,
kp_driving_initial=kp_driving_initial, use_relative_movement=relative,
use_relative_jacobian=relative, adapt_movement_scale=adapt_movement_scale)
out = generator(source, kp_source=kp_source, kp_driving=kp_norm)
predictions.append(np.transpose(out['prediction'].data.cpu().numpy(), [0, 2, 3, 1])[0])
return predictions
def find_best_frame(source, driving, cpu=False):
import face_alignment
def normalize_kp(kp):
kp = kp - kp.mean(axis=0, keepdims=True)
area = ConvexHull(kp[:, :2]).volume
area = np.sqrt(area)
kp[:, :2] = kp[:, :2] / area
return kp
fa = face_alignment.FaceAlignment(face_alignment.LandmarksType._2D, flip_input=True,
device='cpu' if cpu else 'cuda')
kp_source = fa.get_landmarks(255 * source)[0]
kp_source = normalize_kp(kp_source)
norm = float('inf')
frame_num = 0
for i, image in tqdm(enumerate(driving)):
kp_driving = fa.get_landmarks(255 * image)[0]
kp_driving = normalize_kp(kp_driving)
new_norm = (np.abs(kp_source - kp_driving) ** 2).sum()
if new_norm < norm:
norm = new_norm
frame_num = i
return frame_num
def h_interface(input_image: str):
parser = ArgumentParser()
opt = parser.parse_args()
opt.config = "./config/vox-256.yaml"
opt.checkpoint = "./checkpoint/vox-cpk.pth.tar"
opt.source_image = input_image
opt.driving_video = "./data/input/ts.mp4"
opt.result_video = "./data/result/{}.mp4".format(uuid.uuid1().hex)
opt.relative = True
opt.adapt_scale = True
opt.cpu = True
opt.find_best_frame = False
opt.best_frame = False
# source_image = imageio.imread(opt.source_image)
source_image = opt.source_image
reader = imageio.get_reader(opt.driving_video)
fps = reader.get_meta_data()['fps']
driving_video = []
try:
for im in reader:
driving_video.append(im)
except RuntimeError:
pass
reader.close()
source_image = resize(source_image, (256, 256))[..., :3]
driving_video = [resize(frame, (256, 256))[..., :3] for frame in driving_video]
generator, kp_detector = load_checkpoints(config_path=opt.config, checkpoint_path=opt.checkpoint, cpu=opt.cpu)
if opt.find_best_frame or opt.best_frame is not None:
i = opt.best_frame if opt.best_frame is not None else find_best_frame(source_image, driving_video, cpu=opt.cpu)
print("Best frame: " + str(i))
driving_forward = driving_video[i:]
driving_backward = driving_video[:(i + 1)][::-1]
predictions_forward = make_animation(source_image, driving_forward, generator, kp_detector,
relative=opt.relative, adapt_movement_scale=opt.adapt_scale, cpu=opt.cpu)
predictions_backward = make_animation(source_image, driving_backward, generator, kp_detector,
relative=opt.relative, adapt_movement_scale=opt.adapt_scale, cpu=opt.cpu)
predictions = predictions_backward[::-1] + predictions_forward[1:]
else:
predictions = make_animation(source_image, driving_video, generator, kp_detector, relative=opt.relative,
adapt_movement_scale=opt.adapt_scale, cpu=opt.cpu)
imageio.mimsave(opt.result_video, [img_as_ubyte(frame) for frame in predictions], fps=fps)
return opt.result_video
if __name__ == "__main__":
demo = gr.Interface(h_interface, inputs=[gr.Image(shape=(500, 500))], outputs=[gr.Video()])
demo.launch()
# h_interface("C:\\Users\\huyi\\Desktop\\xx3.jpg")
代码说明
1、将原demo.py中的main函数内容,重新编辑为h_interface方法,输入是想要驱动的图片。
2、其中driving_video参数使用了我自己录制的一段表情视频ts.mp4,我建议在使用的时候可以自己用手机录制一段替换。
3、使用gradio来生成方法的页面,下面会展示给大家看。
4、使用uuid为结果视频命名。
执行结果如下
Running on local URL: http://127.0.0.1:7860/
To create a public link, set `share=True` in `launch()`.
打开本地的地址:http://localhost:7860/
可以看到我们实现的交互界面如下:
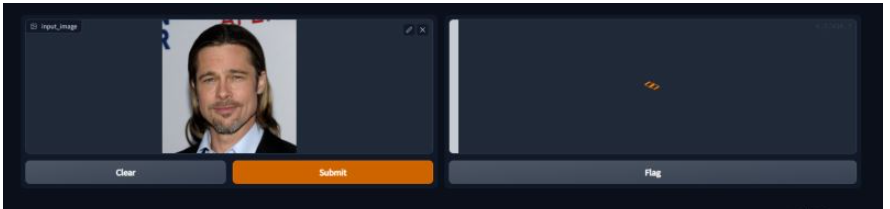
我们上传一下我准备的样例图片,提交制作。
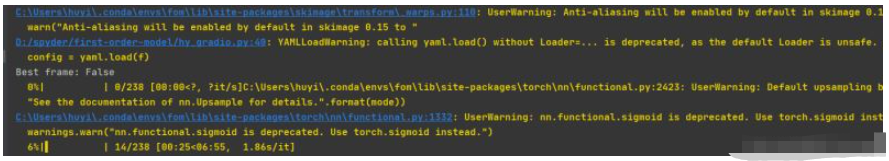
看一下执行的日志,如下图。
看一下制作结果。
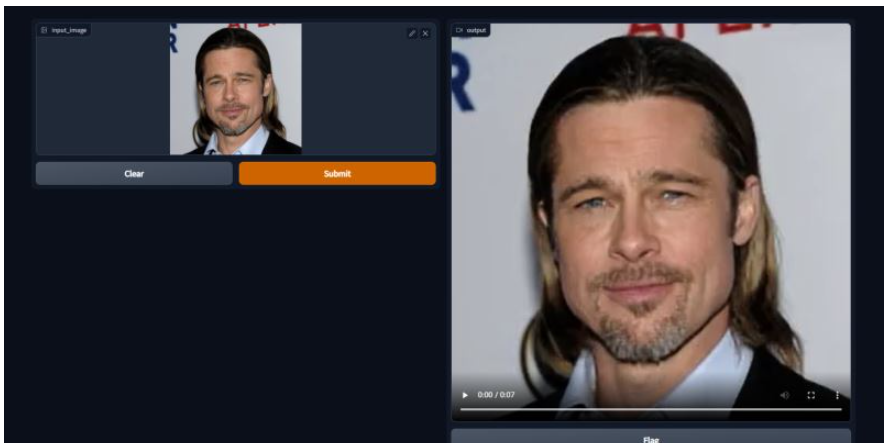
由于上传不了视频,我将视频转成了gif。

关于“Python first-order-model怎么实现让照片动起来”的内容就介绍到这里了,感谢大家的阅读。如果想了解更多行业相关的知识,可以关注蜗牛博客行业资讯频道,小编每天都会为大家更新不同的知识点。
免责声明:本站发布的内容(图片、视频和文字)以原创、转载和分享为主,文章观点不代表本网站立场,如果涉及侵权请联系站长邮箱:niceseo99@gmail.com进行举报,并提供相关证据,一经查实,将立刻删除涉嫌侵权内容。














评论